Here's Why Apple Is Building Solar Farms in China
 Apple just agreed to back two large solar farms in China. It’s the biggest deal of its kind for a U.S. company operating in China. For China, the deal is only a beginning.
Apple just agreed to back two large solar farms in China. It’s the biggest deal of its kind for a U.S. company operating in China. For China, the deal is only a beginning. China has been installing more renewable-power capacity than fossil fuels for several years, a gap that's growing. In 2015, China will install 15 gigawatts to 18 gw of solar power alone, double the solar deployment in the U.S., according to an analysis by Bloomberg New Energy Finance (BNEF).
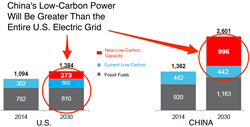
The chart shows how, in the next 15 years, China is on track to have more low-carbon electricity than the entire capacity of the U.S. power grid. "Think of what their grid will look like in 2030," Michael Liebreich, founder of BNEF, said at the organization's annual summit last week in New York. "A very competitive advantage."
For Apple, the 40-megawatt partnership extends Chief Executive Officer Tim Cook's solar aspirations beyond U.S. borders. Cook announced an $850 million deal in February to purchase enough solar to power all its California operations: stores, offices, headquarters, and a data center. By making a similar push in China, the tech giant begins to offset its considerable manufacturing pollution, which is almost entirely overseas.
Many U.S. tech giants—not just Apple—have been criticized for outsourcing their pollution, says Justin Wu, head of Asia research for BNEF. Apple is "hitting back at that whole line of arguments," he says. "This is the beginning of something. Manufacturing in China is going to get greened."
Comments (0)
This post does not have any comments. Be the first to leave a comment below.
Featured Product

Canadian Solar - HiKuBlack - Black Backsheet & Frame (Mono)
Aesthetic appearance for residential systems: With black backsheet & black frame, Power range 380 ~ 405 W, Low power loss in cell connection. Enhanced reliability: · Low temperature coefficient (Pmax): -0.34 % / °C, LID LeTID less than 2.0%, Lower hot spot temperature, Better shading tolerance.
